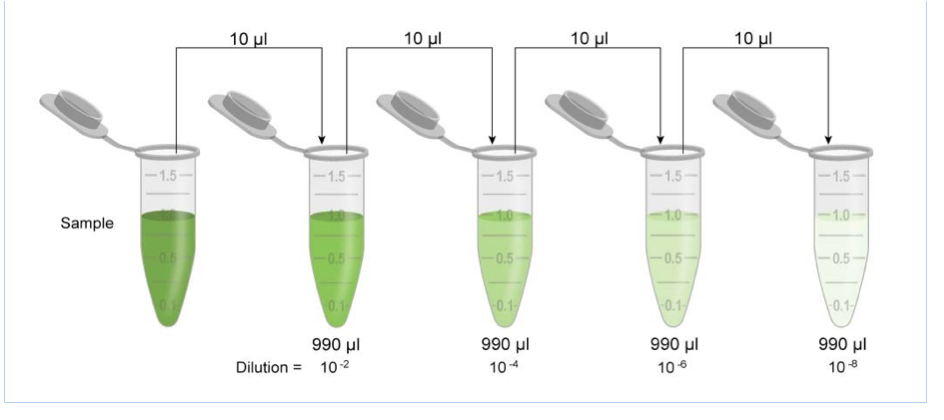


Add a fixed volume of diluent, usually water, to the container to make up the final volume.The container should have a sufficient volume to accommodate the dilution. Transfer the measured volume of the stock solution to a larger container, typically a volumetric flask.This volume will be used as the starting point for the dilution. Measure a fixed volume of the stock solution, usually 1 mL or more.The stock solution should have a known concentration and should be stored appropriately to maintain its stability. Prepare a stock solution of the substance to be diluted.
Serial dilution serial#
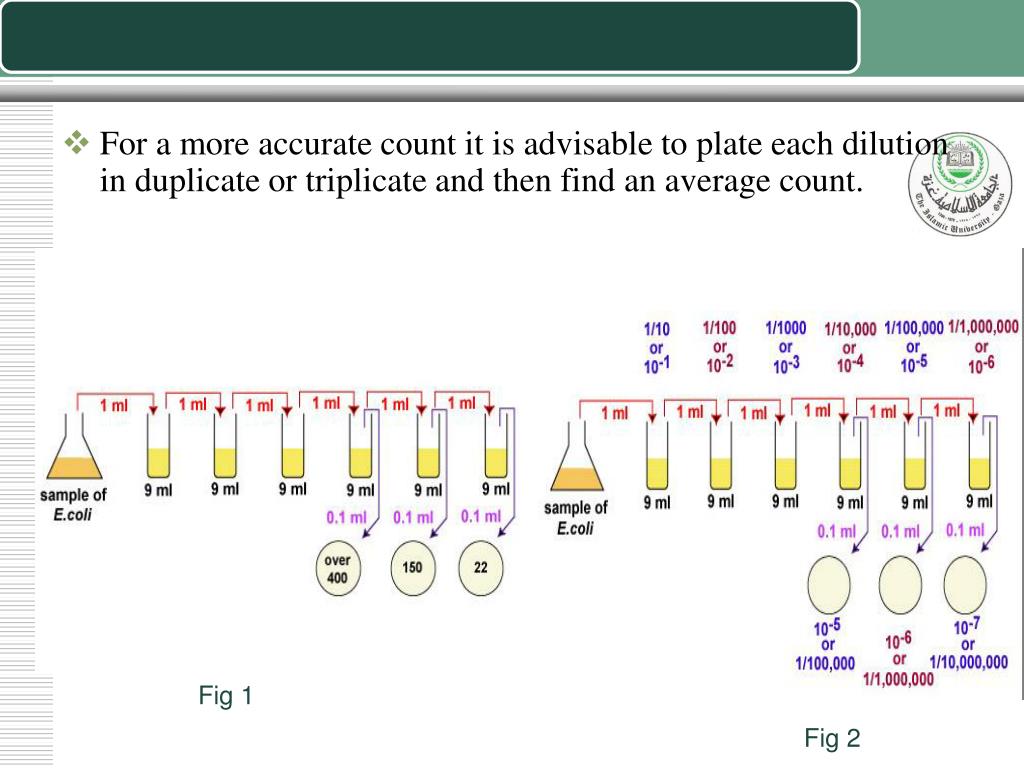
The procedure for serial dilution typically involves the following steps: This equation represents the relationship between the concentration and volume of the solution, and it is used to calculate the concentration of the dilution. The formula for serial dilution is given by: C1V1 = C2V2 Where C1 and C2 represent the initial and final concentrations of the substance, and V1 and V2 represent the corresponding volumes of the solutions. This process is repeated several times to obtain a series of solutions with progressively lower concentrations. Serial dilution is the process of diluting a substance in a solution in a fixed proportion, resulting in a series of solutions with decreasing concentrations of the substance. In this article, we will discuss the definition, formula, procedure, calculator, and uses of serial dilution. This method is widely used in various fields, including microbiology, biochemistry, environmental science, and analytical chemistry, among others. It is a simple and efficient way to create a series of solutions with gradually decreasing concentrations of a particular substance. Serial dilution is a technique used to reduce the concentration of a substance in a solution. Serial Dilution- Definition, Formula, Calculator, Procedure, Uses


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
